Difference between revisions of "TTL ETH"
From Diustou Wiki
Yousimaier17 (talk | contribs) |
Yousimaier17 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
== Product Selection == | == Product Selection == | ||
| − | *[[File:ETH_产品选型.png| | + | *[[File:ETH_产品选型.png|1200px]] |
== User Instructions == | == User Instructions == | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 7 February 2025
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
Contents
Product Features
- Utilizes the original CH9120 chip, which internally incorporates the Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) layer and Physical (PHY) layer.
- Enables bidirectional transparent transmission of serial port data and RJ45 Ethernet port data.
- Supports 10M, full-duplex/half-duplex adaptive Ethernet interface, compatible with the 802.3 protocol.
- Supports MDI/MDIX automatic line conversion, allowing for arbitrary connection of crossover or straight-through cables with automatic switching.
- Supports DHCP for automatic IP address acquisition and DNS domain name access.
- Allows configuration of chip working mode, ports, IP, and other network parameters through host computer software or serial port commands.
- Supports four working modes: TCP CLIENT, TCP SERVER, UDP CLIENT, and UDP SERVER.
- Supports the KEEPALIVE mechanism.
- Supports serial port baud rates ranging from 300bps to 921600bps.
- Serial communication level: 5V
- Equipped with three types of indicator lights:
- Power indicator light (red): Remains on as long as the power supply is connected normally.
- TX transmission indicator light (green): Flashes when data is received via the RJ45 Ethernet port.
- RX reception indicator light (blue): Flashes when data is received via the TTL interface.
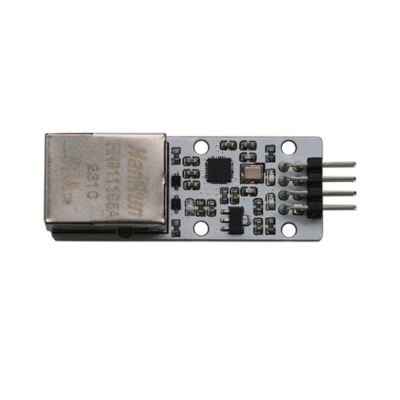
Pin Description
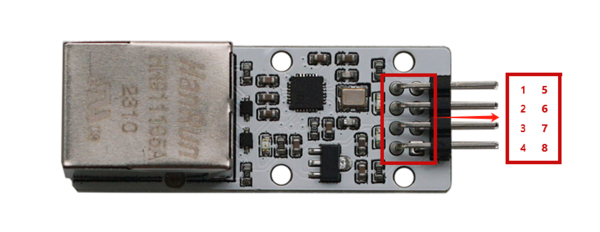
- 1. TCPS: In TCP client mode, indicates connection status; low level indicates successful connection.
- 2. RES: Factory reset pin; when the chip is powered on, holding this pin low for 3 seconds will reset it to factory settings.
- 3. CFGO: Serial port configuration mode setting pin; internally pulled up; when a low level is detected, it enters serial port configuration mode; high level exits configuration mode.
- 4. RSTI: External reset input pin; active low.
- 5. GND: Power supply negative terminal.
- 6. RXD: Serial port data receiving end; connects to the TX pin of a TTL device.
- 7. TXD: Serial port data transmitting end; connects to the RX pin of a TTL device.
- 8. 5V: Power supply positive terminal; connects to 5V.
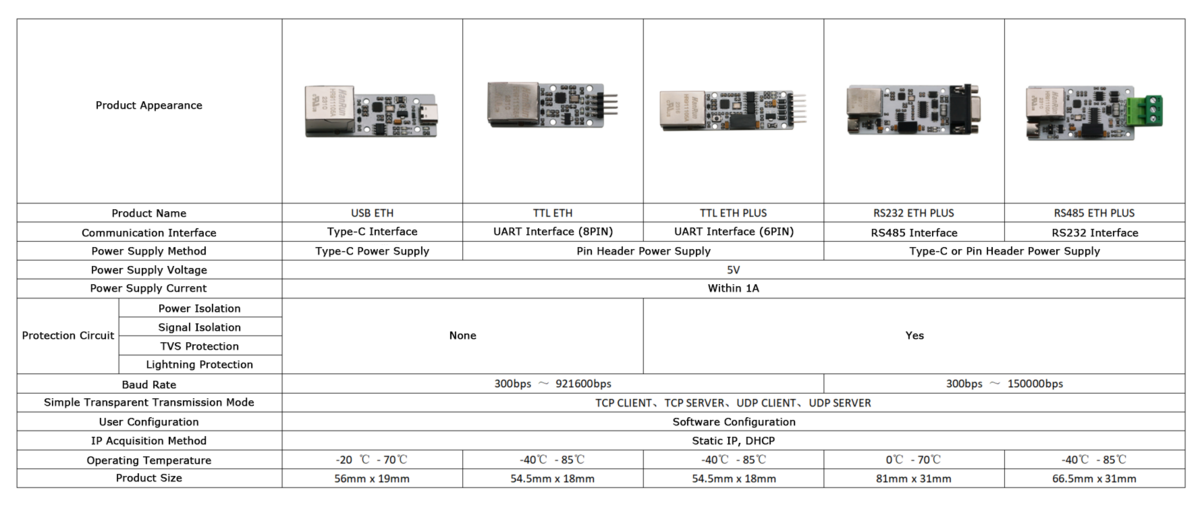
Product Selection
User Instructions
Function Introduction
- CH9120 is a network-to-serial transparent transmission chip that enables bidirectional transparent transmission of serial data and network data. It supports four working modes: TCP CLIENT/SERVER and UDP CLIENT/SERVER. The serial port baud rate supports a range of 300bps to 921600bps. Before use, the network and serial port parameters of the chip need to be configured through host computer software. Once configured, CH9120 saves the configuration parameters to its internal storage space. After resetting, CH9120 will operate according to the saved configuration values.
- The basic parameters of CH9120 include: name, MAC address display, automatic IP address acquisition setting, manual IP address setting (including CH9120 IP address, subnet mask, default gateway), and serial port negotiation configuration. The name is mainly for convenient management of CH9120 modules within the local area network, with a length not exceeding 20 bytes. The MAC address field displays the MAC address of the currently selected module. CH9120 has two ways to set network parameters:
- 1) DHCP, which automatically obtains network parameters from a gateway device with DHCP SERVER functionality;
- 2) Manual setting. The serial port negotiation configuration function refers to the ability to enter the serial port configuration mode through serial port handshaking, which is disabled by default.
- The port parameters of CH9120 include: network mode, local port, target IP/domain name, destination port, serial port baud rate/data bits/stop bits/parity bits, network cable disconnection handling, RX packet length, RX packet timeout interval, and network connection operation. Network mode (TCP SERVER/CLIENT, UDP SERVER/CLIENT), destination IP address, and local/destination port are the basic parameters for network communication. The destination IP address can also be accessed using a domain name.
- The serial port baud rate range of the chip is 300bps to 921600bps (the baud rate error of the serial port transmission signal is less than 0.5%, and the allowed baud rate error of the serial port reception signal is not less than 2%). It supports 5, 6, 7, or 8 data bits, as well as 1 or 2 stop bits. It supports odd, even, no parity, space 0, and mark 1 parity modes.
- Network cable disconnection handling refers to whether CH9120 actively closes the connection internally or takes no action when the network cable is disconnected.
- The RX packet length range is 1 to 512. When the serial port of CH9120 receives data of the set length, CH9120 will immediately package the serial port data and send it out through the network. The timeout setting range is 0 to 200, with a timeout unit of approximately 5ms. For example, when the timeout is set to 1, if the data length in the serial port reception buffer does not reach the RX packet length and no new data is received within 5ms, a serial port timeout occurs. After the serial port timeout, CH9120 will send the data received by the serial port out through the network. When the timeout is set to 0, an internal hardware timeout (no new data received for more than 4 data times) mechanism is enabled, which is suitable for scenarios with high real-time requirements and large-scale data transmission and reception.
- The setting for clearing the serial port buffer refers to how to handle data received by the serial port before the network connection is established. It can be cleared (discarded) or retained when a TCP connection is established.
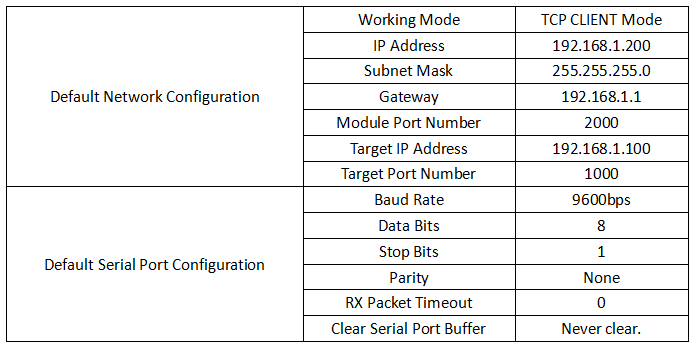
Default Configuration
Product Testing
Note: If you encounter issues with Ethernet port connectivity, please try the following steps:
- Disable the firewall and antivirus software on your computer (usually found in the Control Panel), and also close any security software such as Safe Guard if installed.
- Check the hardware connections for any errors, such as ensuring the Ethernet port is securely connected and the Ethernet cable is functioning properly.
- Verify that the IP address of your computer is on the same subnet as the IP address of the module.
Hardware Preparation
- Dupont wires Several
- Ethernet cable x1
- PC x1
- USB to TTL or serial cable x1
- TTL ETH x1
Testing Method
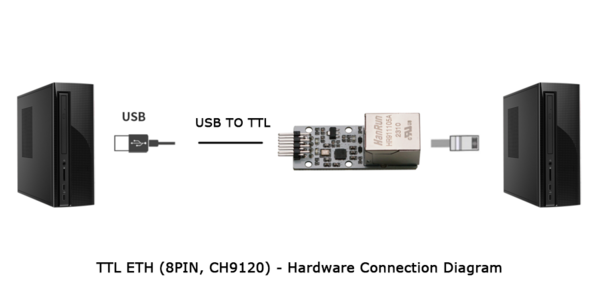
Direct Connection with Computer
- Hardware Connection:
Note: If there is no serial port module or cable, you can power the TTL ETH module using a 5V power supply module and then short-circuit the TXD and RXD of the TTL ETH module together for self-transmission and reception testing.
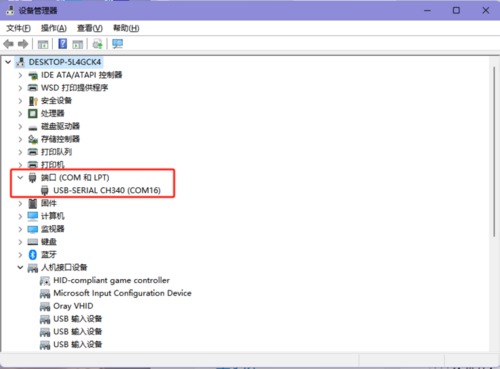
- Install Driver:
- Download the CH340 driver and install it.
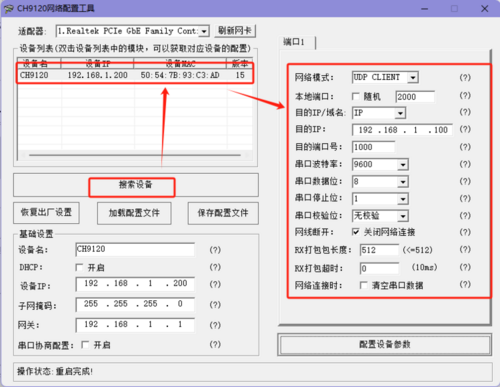
- View Module Configuration:
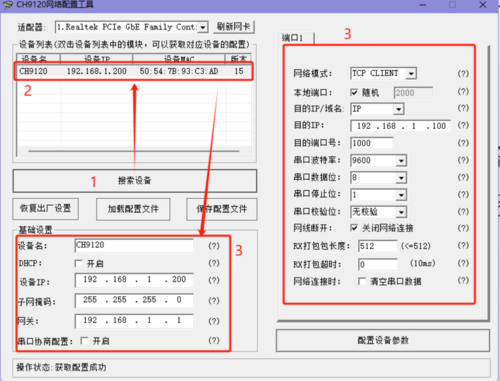
- Open the Network Configuration Software
, click "Search Device", and the searched devices will appear in the upper dialog box. Double-click the searched device, and the corresponding device configuration information will appear below and to the right of the software.
- Modify Computer IP Address:
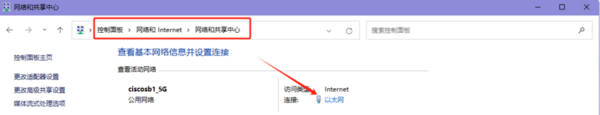
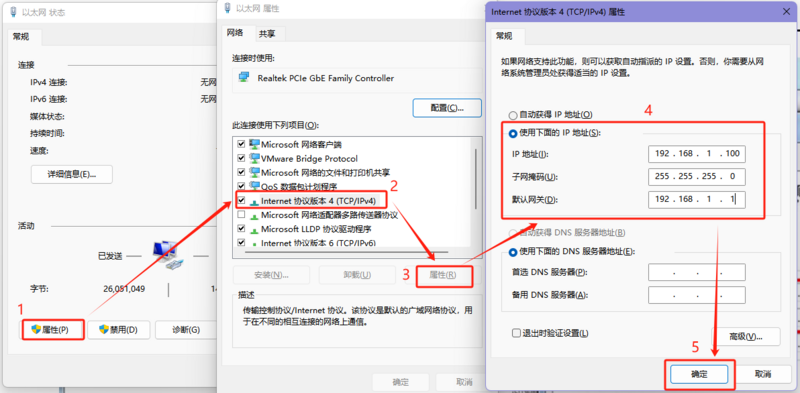
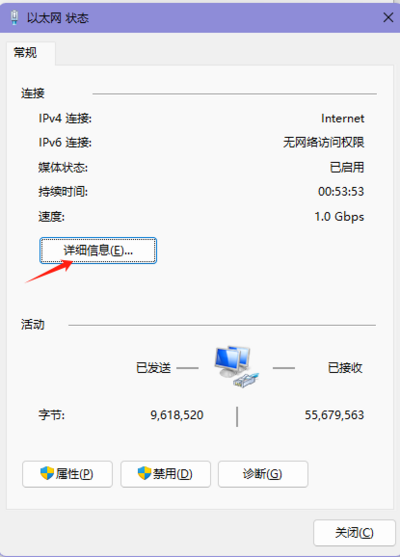
- Control Panel (File Explorer) -> Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center -> Double-click the network connection -> Properties -> Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) -> Properties -> Use the IP address below, configure the computer's IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway, then click OK.
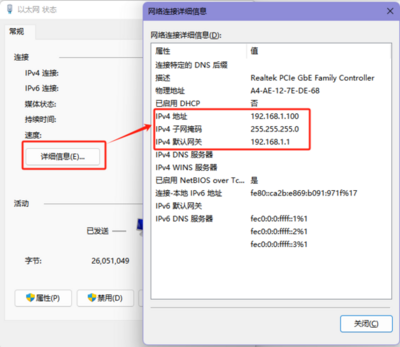
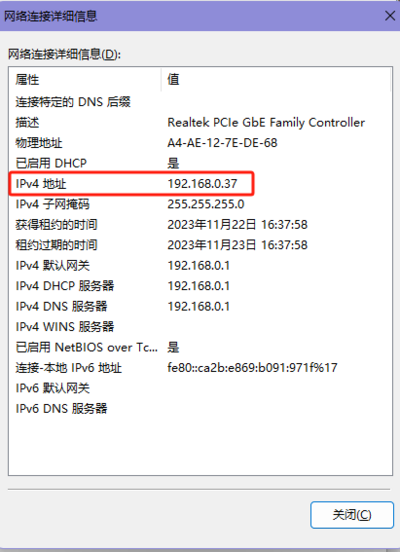
- After setting, you can check if the computer's IP is successfully set by going to Control Panel (File Explorer) -> Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center -> Double-click the network connection -> Details.
- Communication Test:
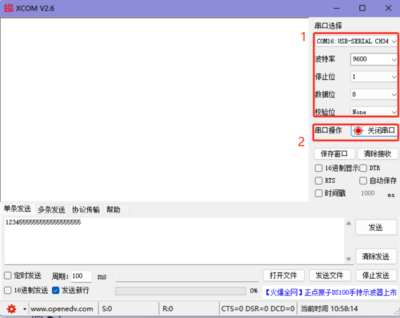
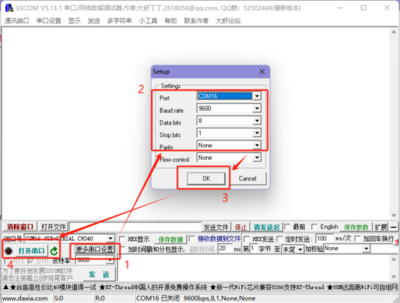
- Open the Serial Port Debugging Assistant, select the corresponding port (viewable through Device Manager), set the serial port baud rate (default for the module is 9600), stop bits (default is 1), data bits (default is 8), and parity (default is None), then open the serial port.
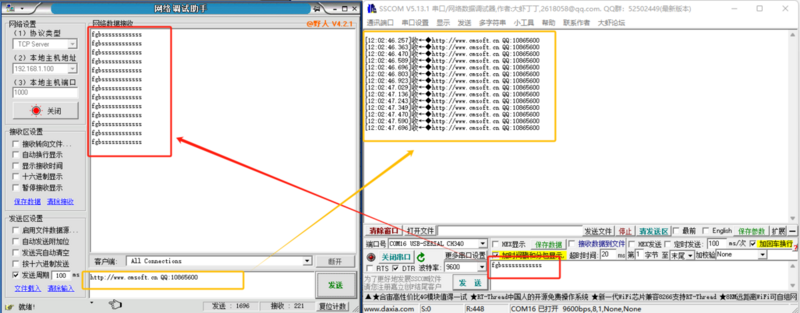
- Open the Network Debugging Assistant, configure the network parameters, click Open to establish a connection.
- Protocol Type: Configure according to the module's working mode. The default working mode of the module here is TCP CLIENT, so the protocol type is set to TCP Server.
- Local Host Address: Set it according to the actual computer IP address. Here, the computer IP is 192.168.1.100.
- Local Host Port: Set it according to the destination port number configured when setting up the module. Here, it is the default value of 1000.
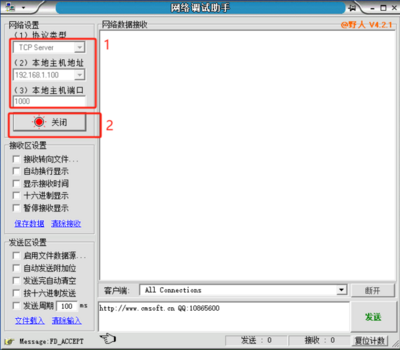
- Use the network debugging assistant and serial port debugging assistant to send data respectively, and check if the data is correctly received on the other end.
Connecting to the Router
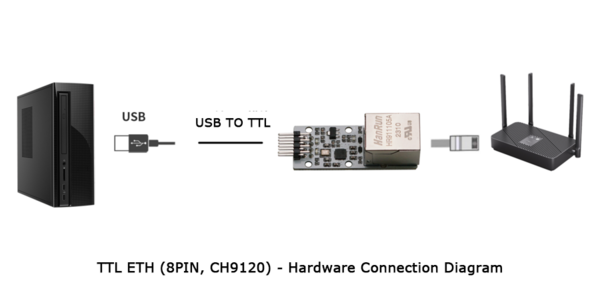
- Hardware Connection:
- Connect the Ethernet port of the TTL ETH module and the Ethernet port of the computer to the same router port using Ethernet cables.
- Connect the TTL interface of the TTL ETH module to the USB interface of the computer via a USB-to-TTL module or a serial cable, using 4 wires (5V to 5V, TXD to RXD, RXD to TXD, GND to GND).
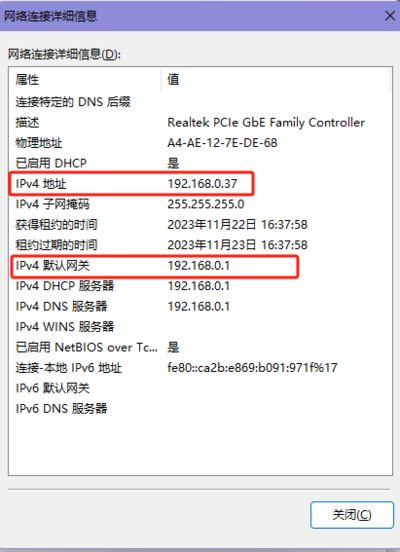
- Checking the Computer's IP Address:
- Installing the Driver:
- Download the CH340 driver and install it.
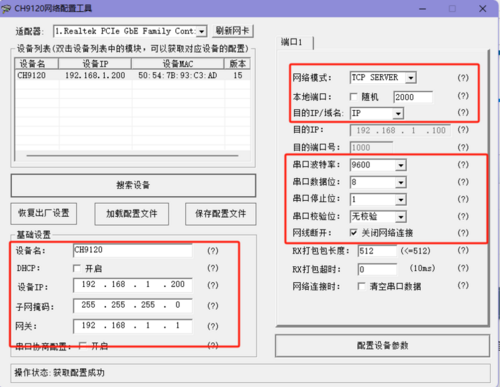
- Changing Module Configuration:
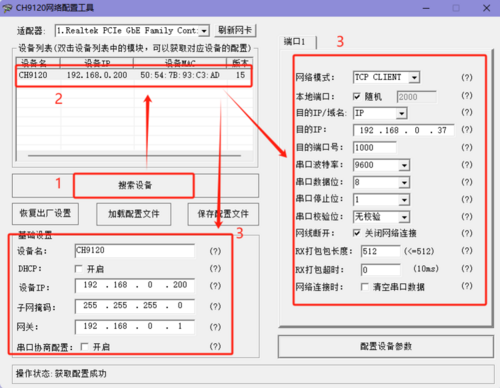
- Open the Network Configuration Software, click "Search Device", and the searched devices will appear in the dialog box above. Double-click the searched device, and the corresponding device configuration information will appear below and to the right of the software.
- Modify the device IP, gateway, destination IP, and destination port number respectively. After making the modifications, click "Configure Parameter Settings" and wait for the setup to complete.
- Device IP: Set it to an IP in the same subnet as the computer. Here, the computer's IP is 192.168.0.37, so set the module IP to 192.168.0.200. Also, when setting the IP address, ensure that the chosen IP is not already in use.
- Gateway: Set the gateway corresponding to the IP address.
- Destination IP: Set it based on the actual connected computer's IP address. Here, the computer's IP is 192.168.0.37.
- Destination Port Number: Modify as needed. The default value of 1000 is used here.
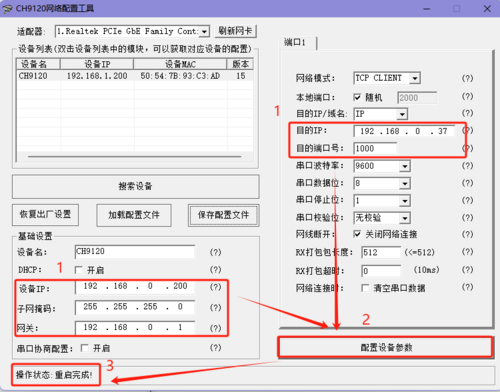
- After configuration, click "Search Device" again, double-click the searched device, and check if the configuration was successful.
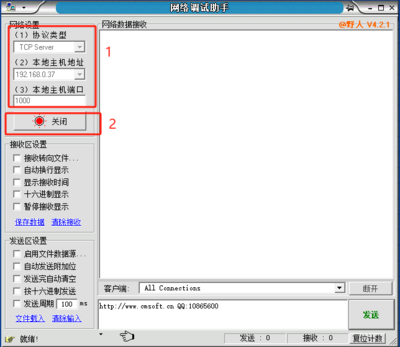
- Communication Test:
- Open the Serial Port Debugging Assistant, select the corresponding port (viewable through Device Manager), set the serial port baud rate (default is 9600), stop bits (default is 1), data bits (default is 8), and parity (default is None), and open the serial port.
- Open the Network Debugging Assistant, configure the network parameters, click "Open" to establish a connection.
- Protocol Type: Configure according to the module's working mode. The default working mode of the module here is TCP CLIENT, so set the protocol type to TCP Server.
- Local Host Address: Set it based on the actual computer's IP address. Here, the computer's IP is 192.168.0.37.
- Local Host Port: Set it based on the destination port number configured when setting up the module. Here, the default value is 1000.
- Use the network debugging assistant and serial port debugging assistant to send data respectively, and check if the data is correctly received on the other end.
Mode Description
TCP SERVER
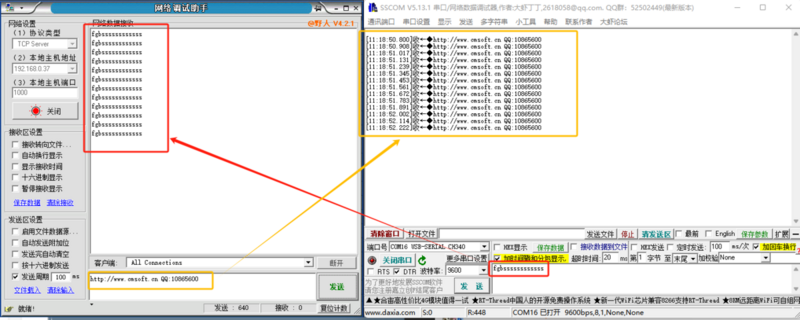
- TCP Server refers to a TCP server. In TCP Server mode, the module listens on a local port, accepts and establishes connections for incoming connection requests, and communicates data. When the module receives data via the serial port, it simultaneously sends the data to the client device connected to the module. This is typically used for communication with TCP clients within a local area network. Like TCP Client, it distinguishes between connected and disconnected states to ensure reliable data exchange.
- When the module operates as a TCP Server, it first listens on the set local port, responds to connection requests, and establishes connections. Upon receiving data via the serial port, it sends the data to the device connected via the TTL Ethernet port. It can accept up to 1 TCP Client connection.
- When the module operates as a TCP Server, it actively listens on the local port number and does not monitor the connected IP addresses or port numbers. When the number of connections exceeds the maximum, it actively disconnects the oldest connection.
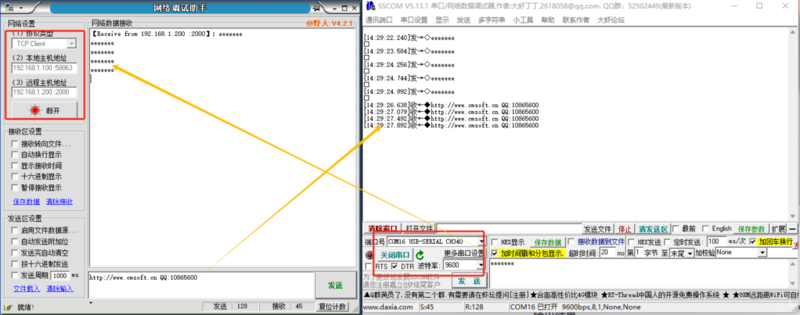
- Application Example:
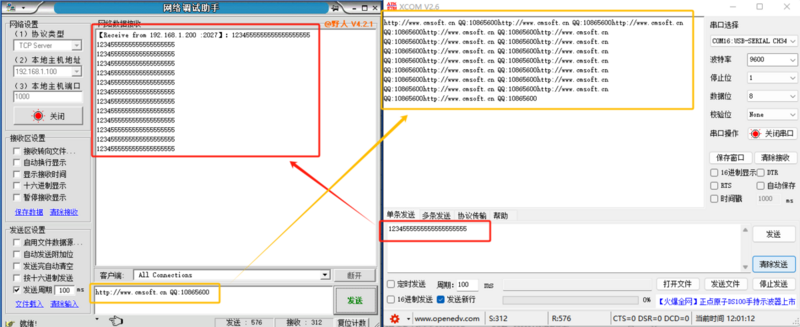
- Set the module's operating mode to TCP Server with a local port number of 2000 and a random remote port number. Click to configure device parameters, and after setting, search for the device. Upon finding the module, verify if the set parameters are correct.
- Open the module's Ethernet port and connect to a network debugging assistant on a PC. Set the protocol type to TCP Client, with the PC's IP address as 192.168.1.100 and the remote host address as 192.168.1.200 on port 2000, then establish a connection.
- Set the correct serial port parameters, click to open the serial port, click to send, and receive bi-directional transparently transmitted data.
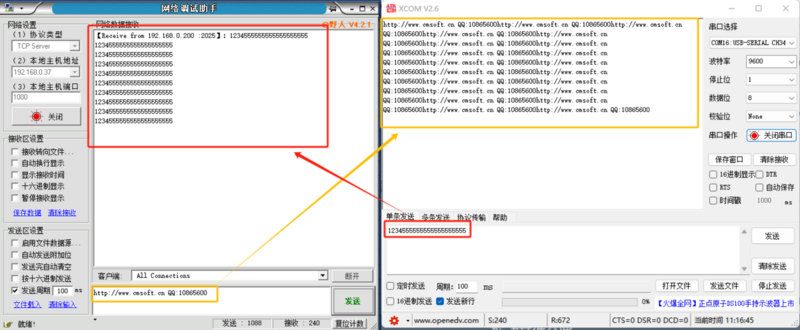
TCP CLIENT
- TCP Client refers to a TCP client. It initiates connections and connects to a server to facilitate the exchange of serial port data with server data. According to the relevant provisions of the TCP protocol, TCP Client distinguishes between connected and disconnected states to ensure reliable data exchange. It is commonly used for data interaction between devices and servers and is the most frequently used method for networked communication.
- When the module operates as a TCP Client, it needs to connect to a TCP Server. The parameters that need to be considered are the destination IP and destination port number. The destination IP should be a device within the same local network.
- When the module operates as a TCP Client, it actively connects to the target port of the target IP and does not accept any other connection requests.
- When the module operates as a TCP Client, the local port number of the TTL ETH should be set to random. This allows the TTL ETH to access the server using a random port number, which can resolve issues where the server may deem the connection status as abnormal and block reconnection requests from the TTL ETH, leading to reconnection failures.
- Application Example:
- Set the module's operating mode to TCP Client, with a destination IP of 192.168.1.100, a remote port number of 1000, and a local port number set to random. Click to configure device parameters, and after setting, search for the device. Upon finding the module, verify if the set parameters are correct.
- Open the module's Ethernet port and connect to a network debugging assistant on a PC. Set the protocol type to TCP Server, with the PC's IP address as 192.168.1.100 and the listened-on port number as 1000. The testing software's network end displays connection information: 192.168.1.200:2093 (randomly assigned port number).
- Set the correct serial port parameters, click to open the serial port, click to send, and receive bi-directional transparently transmitted data.
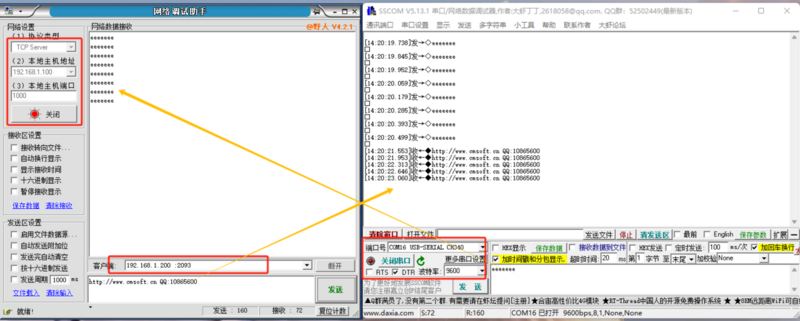
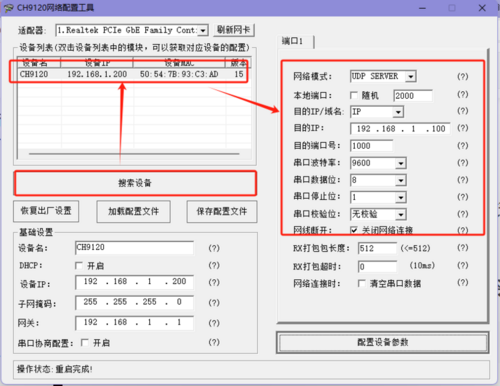
UDP SERVER
- A UDP Server operates on the basis of standard UDP without verifying the source IP address. After receiving each UDP data packet, it changes the destination IP to the source IP and port number. When sending data, it sends to the most recently communicated IP and port number.
- This mode is typically used in scenarios where multiple network devices need to communicate with the module and TCP data transmission is not preferred due to high speed and frequency requirements.
- Application Example:
- Set the module's operating mode to UDP Server, with a destination IP of 192.168.1.100, a remote port number of 1000, and a local port number of 2000. Click to configure device parameters, and after setting, search for the device. Upon finding the module, verify if the set parameters are correct.
- Open the module's Ethernet port and connect to a network debugging assistant on a PC. Set the protocol type to UDP, with the PC's IP address as 192.168.1.100 and the listened-on port number as 1000, to establish a connection.
- Set the correct serial port parameters, click to open the serial port, click to send via serial port. After the network debugging assistant receives the serial port data, the remote host will change to the module's IP and port. Then click to send via network, sending data to the serial port.
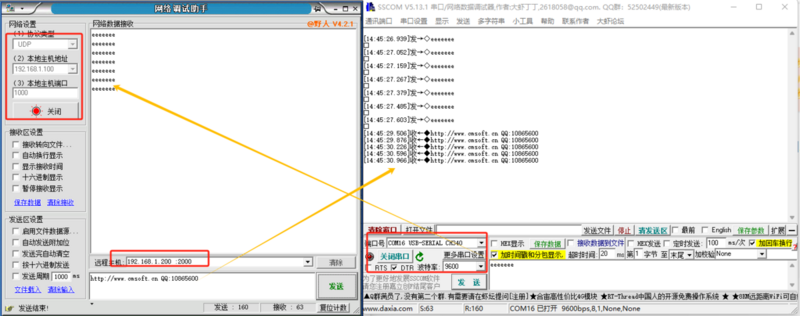
UDP CLIENT
- UDP Client is a connectionless transport protocol that provides a simple, unreliable message delivery service for transactions. There is no establishment or disconnection of connections; data can be sent to the recipient simply by specifying the IP and port. It is commonly used in data transmission scenarios where packet loss rate is not a requirement, data packets are small, sending frequency is high, and data needs to be transmitted to a specified IP.
- In UDP Client mode, the module will only communicate with the target port number of the target IP. If data does not come from this channel, it will not be received by the TTL ETH.
- Application Example:
- Set the module's operating mode to UDP Client, with a destination IP of 192.168.1.100, a remote port number of 1000, and a local port number of 2000. Click to configure device parameters, and after setting, search for the device. Upon finding the module, verify if the set parameters are correct.
- Open the module's Ethernet port and connect to a network debugging assistant on a PC. Set the protocol type to UDP, with the PC's IP address as 192.168.1.100 and the listened-on port number as 1000, to establish a connection.
- Set the correct serial port parameters, click to open the serial port, click to send via serial port. After the network debugging assistant receives the serial port data, the remote host will change to the module's IP and port. Then click to send via network, sending data to the serial port.