Difference between revisions of "1.3inch LCD HAT"
m (Text replacement - "\{\{Amazon \|More.*More\]\}\}" to "") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Product | + | {{Product |
|images=[[File:1.3inch-LCD-HAT-1.jpg|300px| link=https://{{SERVERNAME}}/1.3inch-lcd-hat.htm]] | |images=[[File:1.3inch-LCD-HAT-1.jpg|300px| link=https://{{SERVERNAME}}/1.3inch-lcd-hat.htm]] | ||
|caption=1.3inch IPS LCD HAT, SPI interfaces | |caption=1.3inch IPS LCD HAT, SPI interfaces | ||
|categories=[[:Category:OLEDs / LCDs|OLEDs / LCDs]], | |categories=[[:Category:OLEDs / LCDs|OLEDs / LCDs]], | ||
|brand=Waveshare | |brand=Waveshare | ||
| − | | | + | |interfaces={{Category|SPI}} |
| − | |||
| − | {{ | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
This is an IPS LCD display HAT for Raspberry Pi, 1.3inch diagonal, 240x240 pixels, with embedded controller, communicating via SPI interface. | This is an IPS LCD display HAT for Raspberry Pi, 1.3inch diagonal, 240x240 pixels, with embedded controller, communicating via SPI interface. | ||
| − | |||
==Specification== | ==Specification== | ||
| Line 91: | Line 88: | ||
== Datasheet == | == Datasheet == | ||
*[[:File:ST7789_Datasheet.pdf|ST7789VM]] | *[[:File:ST7789_Datasheet.pdf|ST7789VM]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==FAQ== | ==FAQ== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 22 March 2021
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Contents
Introduction
This is an IPS LCD display HAT for Raspberry Pi, 1.3inch diagonal, 240x240 pixels, with embedded controller, communicating via SPI interface.
Specification
- Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V
- Interface: SPI
- LCD type: IPS
- Controller: ST7789VM
- Resolution: 240(H)RGB x 240(V)
- Display size: 23.4(H)x 23.4(V)mm
- Pixel size: 0.0975(H)x 0.0975(V)mm
- Dimension: 65 x 30.2(mm)
Pinout
| PIN | Raspberry Pi Interface (BCM) | Description |
| KEY1 | P21 | KEY1GPIO |
| KEY2 | P20 | KEY2GPIO |
| KEY3 | P16 | KEY3GPIO |
| Joystick UP | P6 | Upward direction of the Joystick |
| Joystick Down | P19 | Downward direction of the Joystick |
| Joystick Left | P5 | Left direction of the Joystick |
| Joystick Right | P26 | Right direction of the Joystick |
| Joystick Press | P13 | Press the Joystick |
| SCLK | P11/SCLK | SPI clock line |
| MOSI | P10/MOS | SPI data line |
| CS | P8/CE0 | Chip selection |
| DC | P25 | Data/Command control |
| RST | P27 | Reset |
| BL | P24 | Backlight |
LCD and the controller
The ST7789VW is a single-chip controller/driver for 262K-color, graphic type TFT-LCD. It consists of 240 source line and 320 gate line driving circuits. The resolution of this LCD is 240(H)RGB x 240(V), it supports horizontal mode and vertical mode, and it doesn't use all the RAM of controller. This LCD accepts 8-bits/9-bits/16-bits/18-bits parallel interface, that are RGB444, RGB565, RGB666. The color format used in demo codes is RGB565. This LCD use 4-lines SPI interface for reducing GPIO and fast speed.LCD
Working Protocol
 Note: Different from the traditional SPI protocol, the data line from the slave to the master is hidden since the device only has display requirement.
RESX Is the reset pin, it should be low when powering the module and be higher at other times;;
CSX is slave chip select, when CS is low, the chip is enabled.
D/CX is data/command control pin, when DC = 0, write command, when DC = 1, write data
SDA is the data pin for transmitting RGB data, it works as the MOSI pin of SPI interface;
SCL worka s the SCLK pins of SPI interface.
SPI communication has data transfer timing, which is combined by CPHA and CPOL.
CPOL determines the level of the serial synchronous clock at idle state. When CPOL = 0, the level is Low. However, CPOL has little effect to the transmission.
CPHA determines whether data is collected at the first clock edge or at the second clock edge of serial synchronous clock; when CPHL = 0, data is collected at the first clock edge.
There are 4 SPI communication modes. SPI0 is commonly used, in which CPHL = 0, CPOL = 0.
Note: Different from the traditional SPI protocol, the data line from the slave to the master is hidden since the device only has display requirement.
RESX Is the reset pin, it should be low when powering the module and be higher at other times;;
CSX is slave chip select, when CS is low, the chip is enabled.
D/CX is data/command control pin, when DC = 0, write command, when DC = 1, write data
SDA is the data pin for transmitting RGB data, it works as the MOSI pin of SPI interface;
SCL worka s the SCLK pins of SPI interface.
SPI communication has data transfer timing, which is combined by CPHA and CPOL.
CPOL determines the level of the serial synchronous clock at idle state. When CPOL = 0, the level is Low. However, CPOL has little effect to the transmission.
CPHA determines whether data is collected at the first clock edge or at the second clock edge of serial synchronous clock; when CPHL = 0, data is collected at the first clock edge.
There are 4 SPI communication modes. SPI0 is commonly used, in which CPHL = 0, CPOL = 0.
Enable SPI interfaces
- Open terminal, use command to enter the configuration page
sudo raspi-config
Choose Interfacing Options -> SPI -> Yes to enable SPI interface
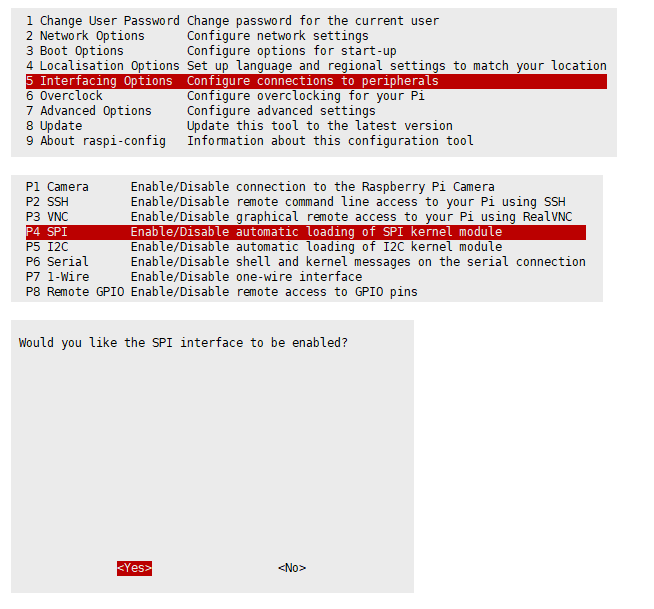 Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Please make sure that SPI interface was not used by other devices, you can check in the /boot/config.txt
Reboot Raspberry Pi:
sudo reboot
Please make sure that SPI interface was not used by other devices, you can check in the /boot/config.txt
Install Libraries
- Install BCM2835 libraries
wget http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/bcm2835-1.68.tar.gz tar zxvf bcm2835-1.68.tar.gz cd bcm2835-1.68/ sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make check && sudo make install For more details, please refer to http://www.airspayce.com/mikem/bcm2835/
- Install Python libraries
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install ttf-wqy-zenhei sudo apt-get install python-pip sudo pip install RPi.GPIO sudo pip install spidev
Download Examples
Open Raspberry Pi terminal and run the following command sudo apt-get install p7zip-full -y wget http://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/b/bd/1.3inch_LCD_HAT_code.7z 7z x 1.3inch_LCD_HAT_code.7z -r -o./1.3inch_LCD_HAT_code sudo chmod 777 -R 1.3inch_LCD_HAT_code cd 1.3inch_LCD_HAT_code
Run the demo
- C
cd c make clean make sudo ./main
- For Raspberry Pi 4B and system version after raspbian_lite-2019-06-20, please set as following for normal input:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
And then add the following line at the end of the config.txt
gpio=6,19,5,26,13,21,20,16=pu
- python
cd python sudo python main.py sudo python key_demo.py
FBCP Transplant
The Framebuffer uses a memory area to store the display content, and changes the data in the memory to change the display content. There is an open-source project on github: fbcp-ili9341. Compared with other fbcp projects, this project uses partial refresh and DMA to achieve a refresh rate of up to 60fps
Compile and Run
sudo apt-get install cmake -y cd ~ wget https://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/2/2d/Fbcp-ili9341.7z sudo apt-get install p7zip-full 7z x Fbcp-ili9341.7z cd Fbcp-ili9341 mkdir build cd build cmake -DSPI_BUS_CLOCK_DIVISOR=20 -DWAVESHARE_ST7789VW_HAT=ON -DDMA_TX_CHANNEL=5 -DDMA_RX_CHANNEL=6 -DBACKLIGHT_CONTROL=ON -DSTATISTICS=0 .. make -j sudo ./fbcp-ili9341 【Note】
- This tutorial is tested on the 2020-12-02-raspios-buster-armhf-full image.
- The selection of cmake doesn't need to be changed in the normal situation, but some programs may occupy DMA channel 5 or 6, which will cause the demo to fail to run.
- If there outputs similar information as below, you need to modify the DMA channel by yourself.
bcm_host_get_peripheral_address: 0xfe000000, bcm_host_get_peripheral_size: 25165824, bcm_host_get_sdram_address: 0xc0000000 BCM core speed: current: 300000000hz, max turbo: 500000000hz. SPI CDIV: 10, SPI max frequency: 50000000hz Allocated DMA channel 7 Allocated DMA channel 1 Enabling DMA channels Tx:7 and Rx:1 DMA hardware register file is at ptr: 0xb52ff000, using DMA TX channel: 7 and DMA RX channel: 1 DMA hardware TX channel register file is at ptr: 0xb52ff700, DMA RX channel register file is at ptr: 0xb52ff100 DMA RX channel 1 was assigned another peripheral map 1! DMA channel 0 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 1 has peripheral map 1 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 1, current control block: 0xff0ea5a0) DMA channel 2 has peripheral map 11 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 1, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 3 has peripheral map 10 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 1, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 4 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 5 has peripheral map 6 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 6 has peripheral map 7 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 7 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 1, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 8 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 1, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 9 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 1, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 10 has peripheral map 0 (is lite channel: 1, currently active: 1, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 11 has peripheral map 13 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 1, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 12 has peripheral map 13 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 13 has peripheral map 13 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA channel 14 has peripheral map 13 (is lite channel: 0, currently active: 0, current control block: (nil)) DMA RX channel was assigned another peripheral map!
- About how to select the cmake, please refer to Readme.md
Auto-start when Power on
sudo cp ~/Fbcp-ili9341/build/fbcp-ili9341 /usr/local/bin/fbcp
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
And then add fbcp& before exit 0, as the picture below.

Set the display resolution
Set the user interface display size in the /boot/config.txt file.
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Then add the following lines at the end of the config.txt. hdmi_force_hotplug=1 hdmi_cvt=300 300 60 1 0 0 0 hdmi_group=2 hdmi_mode=1 hdmi_mode=87 display_rotate=0 【Note】If you are using Raspberry Pi 4B, you need to comment out the following lines on the [pi4] part. The modification is as below: [pi4]
- Enable DRM VC4 V3D driver on top of the dispmanx display stack
- dtoverlay=vc4-fkms-v3d
- max_framebuffers=2
And then reboot the system
sudo reboot
The final display effect is scaled and displayed on the 1.3inch LCD in proportion. The setting of the resolution here should be slightly larger than the LCD resolution, the too high resolution will cause the font display to be blurred. After rebooting the system, the Raspberry Pi OS user interface will be displayed. 600px
Analog mouse
There are a joystick and three buttons on the panel of the module, which we can use to control the mouse of the Raspberry Pi
- Install the library, then download and run the demo
sudo apt-get install python-xlib sudo pip install PyMouse wget http://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/d/d3/Mouse.7z 7z x Mouse.7z sudo python mouse.py 【Note】The mouse.py needs to run under the graphical interface, which will not run under the SSH login. You can skip this step directly, the Pi will run the demo automatically by booting up.
- If you are using the Raspberry PI 4B and the version of your image is after raspbian_lite-2019-06-20, you need to set as below:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
And then add the following line at the end of the config.txt.
gpio=6,19,5,26,13,21,20,16=pu
Use the joystick to move up, down, left, and right, you can see that the mouse is moving.
- Set the auto-start when power on
cd .config/ mkdir autostart cd autostart/ sudo nano local.desktop And then add the following lines at the end of the local.desktop [Desktop Entry] Type=Application Exec=python /home/pi/mouse.py Reboot the system, you can use the buttons to control the mouse.
sudo reboot
Others
If you are interested in getting a game console, you can refer to the following two links: https://www.sudomod.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=11&t=5371&start=10 https://pi0cket.com/guides/tiny-software-for-tinypi/#more-99
Resources
Demo
Relate Resources
Datasheet
FAQ
|
|
Support
|
