Experiment 19: Hall Sensor Experiment
From Diustou Wiki
Revision as of 15:55, 12 February 2025 by Yousimaier17 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "*Basic Experiment Kits For Arduino *Basic Experiment Kits For Raspberry Pi == Arduino == === Experimental Phenomenon === * When a magnetic field is detected, the onboa...")
Contents
Arduino
Experimental Phenomenon
- When a magnetic field is detected, the onboard LED turns on; when no magnetic field is detected, the onboard LED turns off.
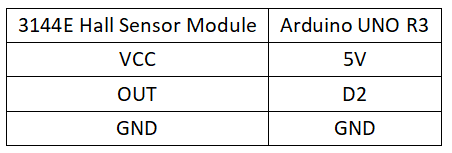
Circuit Connection
传感器说明
- A magnet is required for use.
Reference Program
int Led=13;// Define LED pin
int SENSOR=2; // Define Hall magnetic sensor pin int val
int val;// Define digital variable val
void setup()
{
pinMode(Led,OUTPUT);// Define LED as output pin
pinMode(SENSOR,INPUT);// Define Hall magnetic sensor as input pin
}
void loop()
{
val=digitalRead(SENSOR); // Read the value from digital pin 2 and assign it to val
if(val==LOW) // When the sensor detects a signal, the LED turns on {
digitalWrite(Led, HIGH);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(Led, LOW);
}
}
Raspberry Pi
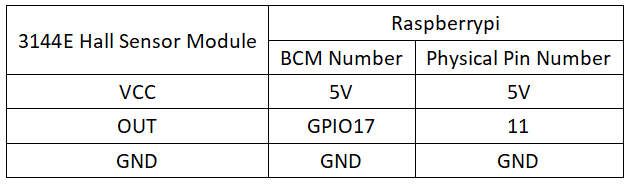
Circuit Connection
Program Execution
Python
- Install the gpiozero library
- You can use the following command to install the library:
sudo apt update sudo apt install python3-gpiozero
- For other systems on the Raspberry Pi, you can use the following command to install the library:
sudo pip3 install gpiozero
- Run the following command to view the GPIO pin definitions on the Raspberry Pi:
pinout
- Download the Raspberry Pi reference example, unzip the file, copy it to the user directory, and run it:
cd raspberrypi/19/python_gpiozero python sensor.py
- You can see the Raspberry Pi running the program correctly. To exit, press ctrl+C.
- Command description: gpiozero.Button(pin, pull_up, active_state, bounce_time, hold_time, hold_repeat)
- Button inherits from DigitalInputDevice and represents a simple button or switch. One end of the button is connected to the ground, and the other end is connected to any GPIO pin; or one end of the button is connected to the 3V3 pin, and the other end is connected to any GPIO pin, and then set pull_up to False in the Button's initialization method.
- Main parameters:
- pin: GPIO pin number;
- pull_up: Internal pull-up/pull-down resistor setting,
- When set to True (default), the GPIO pin is pulled high, and the other end of the button should be connected to ground.
- When set to False, the GPIO pin is pulled low, and the other end of the button should be connected to 3V3.
- When set to None, the GPIO pin is floating, and gpiozero cannot guess the active state, so active_state must be set.
- active_state:
- When set to True, the software pin state is "high" when the hardware pin state is "high".
- When set to False, the input polarity is reversed, and the software pin state is "low" when the hardware pin state is "high".
- When pull_up is set to None, use this parameter to set the unknown pin active state.
- When pull_up is set to True or False, the pin's active state is automatically assigned.
- bounce_time: Software debounce time. Generally, a switch has unstable signals within about 20ms, known as "switch bounce".
- When set to None, software debounce compensation is not performed; otherwise, this parameter is the length of time (in seconds) that the component ignores after the initial change, with a default of 1s.
- hold_time: The time after pressing the button until when_held is triggered, in seconds.
- hold_repeat:
- If True, when_held will continue to be triggered every hold_time seconds as long as the button remains pressed.
- If False, when_held will only be triggered once.
- For more commands, please refer to the gpiozero documentation