Experiment 29: MAX7219 LED Matrix Experiment
From Diustou Wiki
Revision as of 17:31, 12 February 2025 by Yousimaier17 (talk | contribs) (Created page with "*Basic Experiment Kits For Arduino *Basic Experiment Kits For Raspberry Pi == Arduino == === Experimental Phenomenon === * The module cyclically displays patterns when...")
Contents
Arduino
Experimental Phenomenon
- The module cyclically displays patterns when powered on.
Precautions
- When wiring, pay attention to the direction. The left side pin header is the input terminal (1088AS silkscreen is on the top of the PCB board).
- Be mindful of the LED orientation. If the display is abnormal, please reverse the insertion direction.
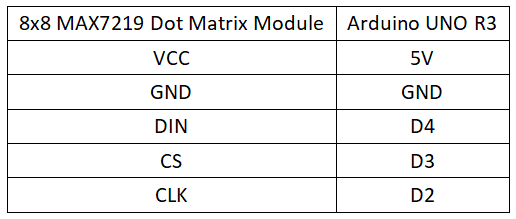
Circuit Connection
Reference Program
#include "LedControl.h"
int DIN = 4;
int CS = 3;
int CLK = 2;
LedControl lc=LedControl(DIN,CLK,CS,0);
void setup(){
lc.shutdown(0,false);
lc.setIntensity(0,15); //Adjust the brightness maximum is 15
lc.clearDisplay(0);
}
void loop(){
//Facial Expression
byte smile[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0xA5,0x99,0x42,0x3C};
byte neutral[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0xBD,0x81,0x42,0x3C};
byte sad[8]= {0x3C,0x42,0xA5,0x81,0x99,0xA5,0x42,0x3C};
//Arrow
byte arrow_up[8]= {0x18,0x3C,0x7E,0xFF,0x18,0x18,0x18,0x18};
byte arrow_down[8]= {0x18,0x18,0x18,0x18,0xFF,0x7E,0x3C,0x18};
//Alternate Pattern
byte d1[8]= {0xAA,0x55,0xAA,0x55,0xAA,0x55,0xAA,0x55};
byte d2[8]= {0x55,0xAA,0x55,0xAA,0x55,0xAA,0x55,0xAA};
//Moving car
byte b1[8]= {0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18,0x3C,0x18,0x3C};//8x8 LED dot matrix pattern generated by software
byte b2[8]= {0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18,0x3C,0x18,0x3C,0x00};
byte b3[8]= {0x00,0x00,0x18,0x3C,0x18,0x3C,0x00,0x00};
byte b4[8]= {0x00,0x18,0x3C,0x18,0x3C,0x00,0x00,0x00};
byte b5[8]= {0x18,0x3C,0x18,0x3C,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00};
byte b6[8]= {0x3C,0x18,0x3C,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18};
byte b7[8]= {0x18,0x3C,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18,0x3C};
byte b8[8]= {0x3C,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x18,0x3C,0x18};
//Moving car
printByte(b1);
delay(50);
printByte(b2);
delay(50);
printByte(b3);
delay(50);
printByte(b4);
delay(50);
printByte(b5);
delay(50);
printByte(b6);
delay(50);
printByte(b7);
delay(50);
printByte(b8);
delay(50);
//alternate pattern
printByte(d1);
delay(100);
printByte(d2);
delay(100);
//Arrow
printByte(arrow_up);
delay(2000);
printByte(arrow_down);
delay(2000);
//Facial Expression
printByte(smile);
delay(1000);
printByte(neutral);
delay(1000);
printByte(sad);
delay(1000);
}
void printByte(byte character [])
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
lc.setRow(0,i,character[i]);
}
}
Raspberry Pi
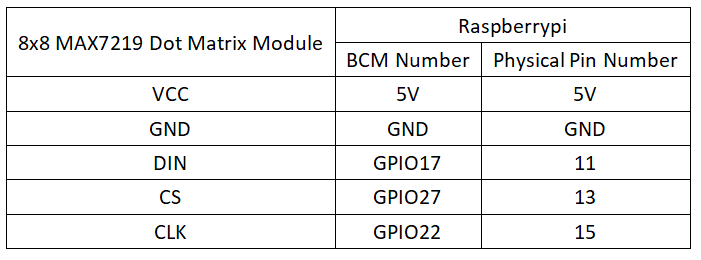
Circuit Connection
Program Execution
Python
- Install the gpiozero library
- You can use the following command to install the library:
sudo apt update sudo apt install python3-gpiozero
- For other systems on the Raspberry Pi, you can use the following command to install the library:
sudo pip3 install gpiozero
- Run the following command to view the GPIO pin definitions on the Raspberry Pi:
pinout
- Download the Raspberry Pi reference example, unzip the file, copy it to the user directory, and run it:
cd raspberrypi/29/python_gpiozero python MAX7219.py
- At this point, you can see the Raspberry Pi running the program correctly. To exit, press ctrl+C.
- Command explanation: gpiozero.OutputDevice(pin, active_high, initial_value)
- Main parameters:
- pin: GPIO pin number
- active_high: Internal pull-up/pull-down resistor setting
- When set to True (default), on() sets the pin to High, and off() sets the pin to LOW.
- When set to False, on() sets the pin to LOW, and off() sets the pin to High.
- initial_value:
- If False (default), all LEDs are initially off.
- If None, the initial state of all LEDs is unstable.
- If True, all LEDs are initially on.
- Main parameters:
- For more commands, please refer to the gpiozero documentation